Roles and Permissions Management
Roles and Permissions in simpleBillBook allow you to control what different users can see and do within the application. This helps maintain security, ensure data integrity, and delegate responsibilities appropriately across your organization.
Overview of Roles and Permissions
Roles and permissions help you:
- Control Access: Determine which users can access specific features
- Protect Data: Prevent unauthorized viewing or modification of sensitive information
- Delegate Responsibilities: Assign appropriate permissions to team members
- Maintain Security: Ensure only authorized personnel can perform critical actions
- Audit Compliance: Track who performed which actions in the system
Viewing Roles
To view all roles:
- Navigate to Manage Users → Roles from the main sidebar
- You'll see a table listing all roles with their associated permissions
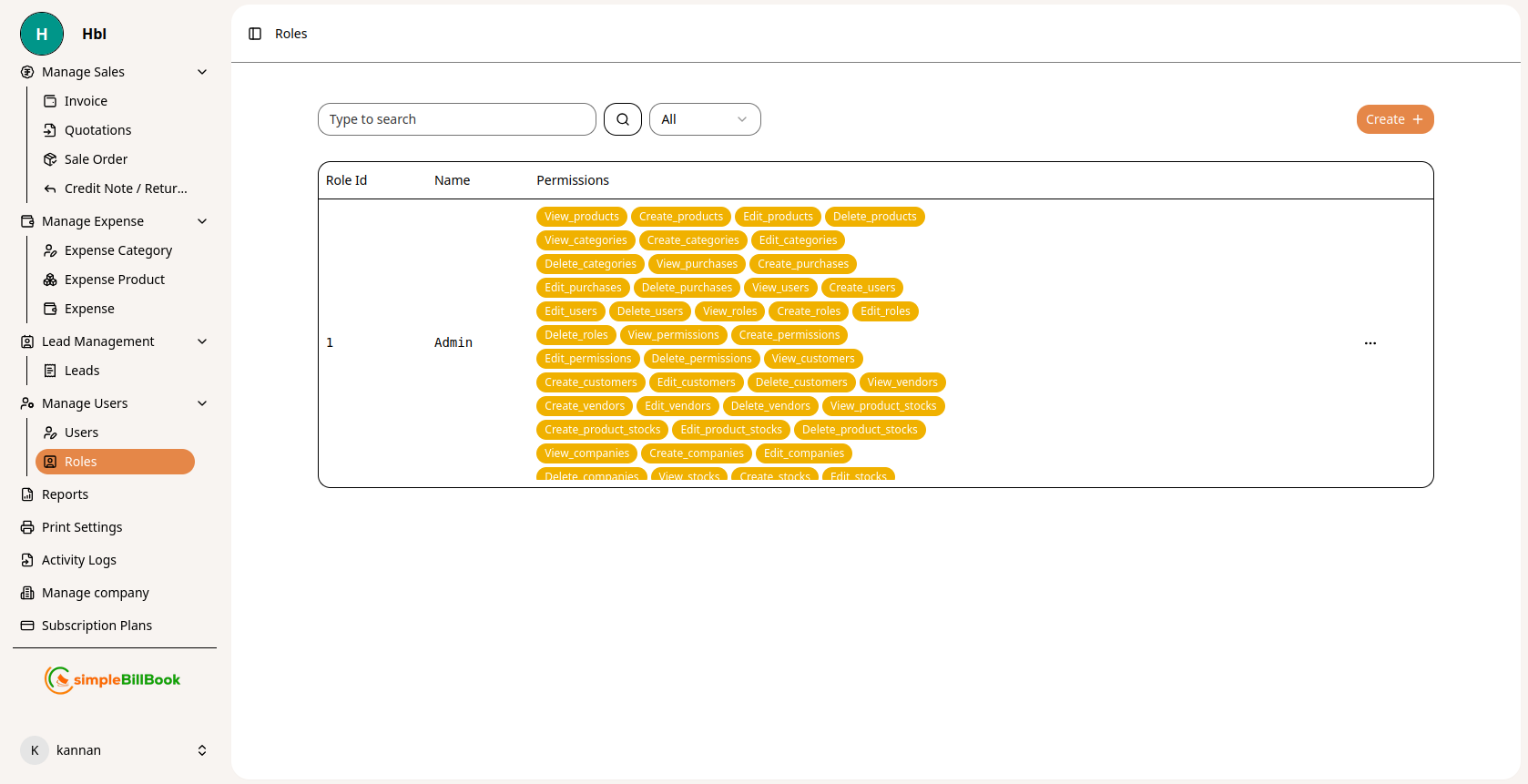 Figure 1: Roles list showing all roles with their permissions
Figure 1: Roles list showing all roles with their permissions
Roles Table Columns:
Role Information:
- Role Id: Unique identifier for each role
- Name: Role name (e.g., Admin, Manager, Sales Representative, Accountant)
- Permissions: Comprehensive list of permissions assigned to the role
Interface Elements:
- Type to search: Search functionality for finding specific roles
- All dropdown: Filter roles if available
- Create +: Button to create new roles
- Pagination: Navigation controls for multiple pages
Understanding Permissions
Permission Structure:
Permissions in the system follow a consistent pattern:
Action Types:
- View: Read/access data
- Create: Add new records
- Edit: Modify existing records
- Delete: Remove records
Module Areas:
1. Products Management
- View products
- Create products
- Edit products
- Delete products
- View product stocks
- Edit product stocks
- Delete product stocks
- Stocks adjust
2. Categories Management
- View categories
- Create categories
- Edit categories
- Delete categories
3. Purchases Management
- View purchases
- Create purchases
- Edit purchases
- Delete purchases
4. Customers Management
- View customers
- Create customers
- Edit customers
- Delete customers
5. Vendors Management
- View vendors
- Create vendors
- Edit vendors
- Delete vendors
6. Users Management
- View users
- Create users
- Edit users
- Delete users
- View employees
- Create employees
- Edit employees
7. Roles & Permissions
- View roles
- Create roles
- Edit roles
- Delete roles
- View permissions
- Create permissions
- Edit permissions
- Delete permissions
8. Companies Management
- View companies
- Create companies
- Edit companies
- Delete companies
9. Activity Logs
- View activity logs
Creating a New Role
Step 1: Access Role Creation
From the roles page, click Create + button to add a new role.
Step 2: Fill Role Details
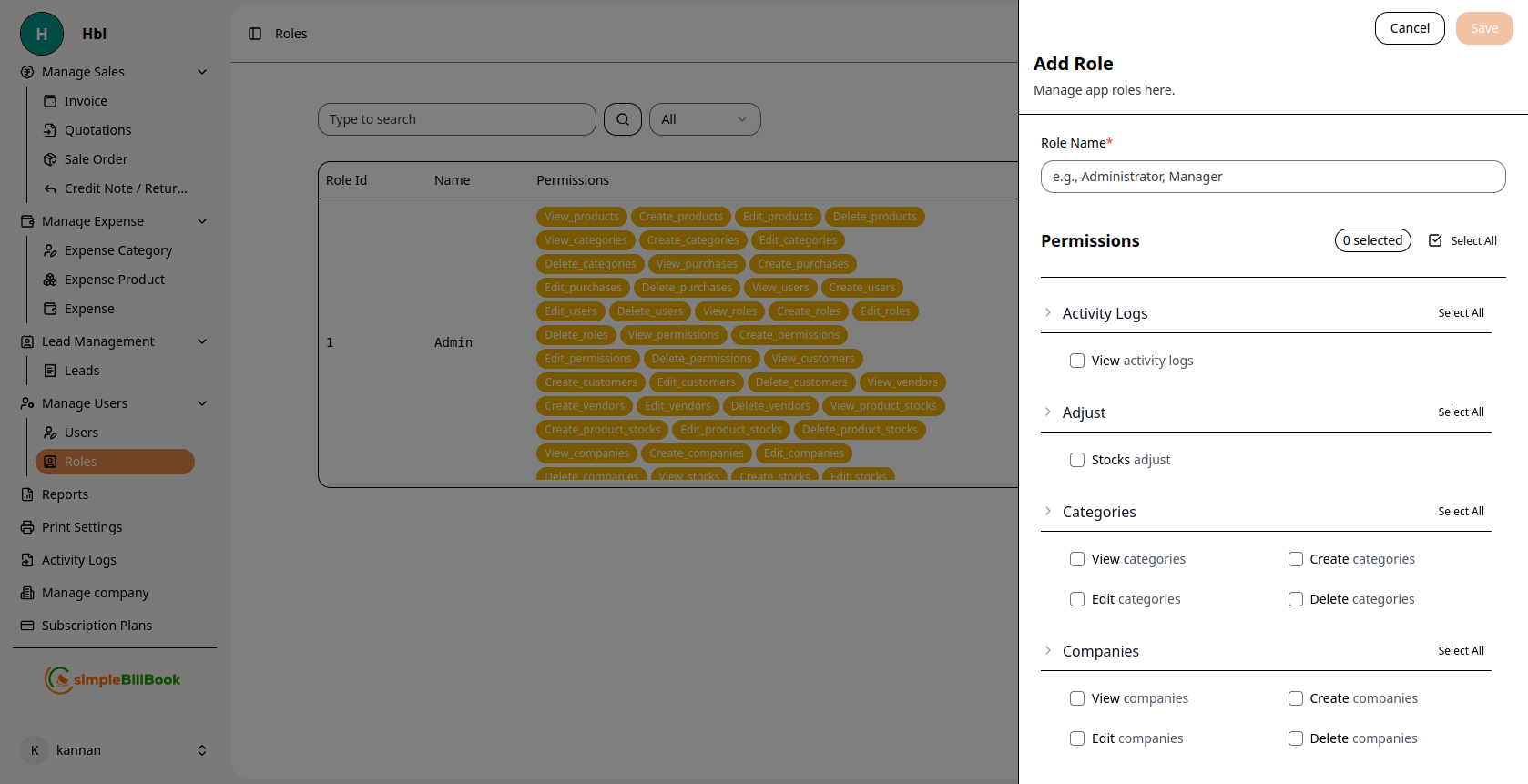 Figure 2: Form for creating new roles with permission checkboxes
Figure 2: Form for creating new roles with permission checkboxes
Required Information:
- Role Name*: Enter a descriptive name for the role (required)
- Examples: Administrator, Manager, Sales Representative, Accountant, Warehouse Staff, Viewer
Step 3: Assign Permissions
Permission Selection Interface:
- Select All: Checkbox to grant all permissions at once
- Category Groups: Permissions organized by module/area
- Individual Permissions: Checkboxes for each specific permission
Permission Categories:
Activity Logs
- View activity logs
Adjust
- Stocks adjust
Categories
- View categories
- Create categories
- Edit categories
- Delete categories
Companies
- View companies
- Create companies
- Edit companies
- Delete companies
(Additional permission categories appear as shown in the interface)
Step 4: Save Role
- Click Save to create the role with selected permissions
- The new role appears in the roles list
- Role becomes available for assignment to users
Default Roles and Their Permissions
1. Admin Role
Description: Full system access with all permissions Typical Permissions:
- All View, Create, Edit, Delete permissions across all modules
- User and role management
- Company settings configuration
- Complete system administration
2. Manager Role
Description: Operational management without system configuration Typical Permissions:
- View, Create, Edit permissions for most modules
- May have limited Delete permissions
- No user/role management
- No company settings access
3. Sales Representative
Description: Customer-facing sales activities Typical Permissions:
- View and Create customers
- View and Create quotations, sales orders, invoices
- View products and inventory
- No financial reporting
- No user management
4. Accountant
Description: Financial transactions and reporting Typical Permissions:
- View and Create purchases, expenses
- View sales transactions
- Financial reports access
- No customer/vendor creation
- No inventory adjustments
5. Warehouse Staff
Description: Inventory management Typical Permissions:
- View and Edit product stocks
- Stocks adjust
- View products and categories
- No sales/purchase creation
- No customer/vendor management
6. Viewer/Read-Only
Description: View data without making changes Typical Permissions:
- View permissions only
- No Create, Edit, Delete permissions
- Ideal for auditors or executives
Best Practices for Role Management
1. Principle of Least Privilege
- Grant only the permissions users need to perform their jobs
- Start with minimal permissions and add as needed
- Regularly review and revoke unnecessary permissions
2. Role-Based, Not User-Based
- Create roles based on job functions, not individuals
- Assign users to appropriate roles
- Avoid creating one-off roles for single users
3. Regular Audits
- Review role assignments quarterly
- Remove users who have changed roles or left the organization
- Verify permissions align with current responsibilities
4. Clear Naming Conventions
- Use descriptive, consistent role names
- Include department or function in role name
- Example: "Sales Manager - West Region" vs. "Manager"
5. Documentation
- Document what each role can access and why
- Maintain approval process for new roles
- Keep record of role changes
6. Segregation of Duties
- Separate conflicting responsibilities
- Example: Person who creates purchase orders shouldn't approve payments
- Prevents fraud and errors
Common Role Structures
Small Business:
├── Admin (Full access) ├── Manager (Operations) └── Staff (Basic transactions)
Medium Business:
├── Administrator (System configuration) ├── Sales Manager (Sales team management) ├── Sales Representative (Customer orders) ├── Purchase Manager (Procurement) ├── Accountant (Financials) └── Warehouse Staff (Inventory)
Enterprise:
├── System Administrator ├── Department Managers (Sales, Purchase, Inventory, Finance) ├── Team Leads ├── Executives (Read-only access) ├── Operations Staff ├── Finance Team ├── Compliance/Audit └── External Accountants (Limited access)
Assigning Roles to Users
Process:
- Navigate to Manage Users → Users
- Select or create a user
- Choose role from dropdown menu
- Save user profile
- User inherits all permissions from assigned role
Multiple Roles:
- Some systems allow users to have multiple roles
- Permissions are cumulative (union of all role permissions)
- Helps when users perform cross-functional duties
Integration with Other Modules
User Management:
- Role Assignment: Each user must have at least one role
- Access Control: User permissions derived from assigned roles
- Audit Trail: Track which users performed which actions
Security:
- Authentication: Who you are (login)
- Authorization: What you can do (roles/permissions)
- Compliance: Meet regulatory requirements for access control
Reporting:
- Permission Reports: Document what each role can access
- User-Role Matrix: Mapping of users to roles
- Access Reviews: Support for compliance audits
Common Scenarios and Solutions
Scenario 1: New Employee Joins
Solution:
- Identify job function and required permissions
- Assign to existing role that matches responsibilities
- Create new role only if existing roles don't fit
Scenario 2: Employee Changes Departments
Solution:
- Remove previous role assignment
- Assign new role matching new responsibilities
- Review and revoke any custom permissions
Scenario 3: Temporary Contractor
Solution:
- Create limited-time role with minimal permissions
- Set account expiration date if supported
- Remove access immediately upon contract completion
Scenario 4: Intern or Trainee
Solution:
- Create "Trainee" role with view-only permissions
- Add create/edit permissions gradually
- Supervised access to sensitive areas
Scenario 5: Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Solution:
- Implement segregation of duties
- Maintain audit trail of all access
- Regular certification of user access
- Document approval processes
Reports and Analytics
Available Role Reports:
- Role Inventory: All roles and their permissions
- User-Role Assignment: Which users belong to which roles
- Permission Coverage: Which permissions are assigned to which roles
- Unused Roles: Roles with no active users
- Role Changes: History of role modifications
Key Metrics to Monitor:
- Number of Roles: Total active roles in system
- Users per Role: Distribution of users across roles
- Permission Count: Number of permissions per role
- Custom Roles: Roles beyond default system roles
- Role Changes: Frequency of role modifications